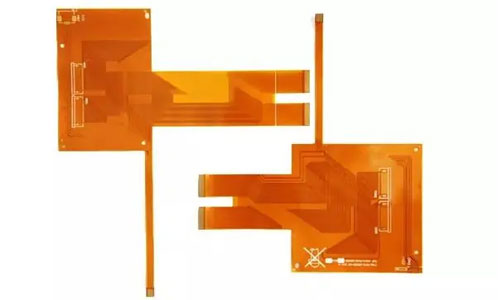
Flex circuit boards, also known as flexible printed circuit boards or flex PCBs, are a type of electronic circuit that offers flexibility in design and enables connection between electronic components. They are composed of flexible, thin, and bendable materials, such as polyimide, which allows them to be shaped and bent to fit into tight or irregular spaces. Flex circuit boards provide several advantages, including space-saving, weight reduction, and increased durability in dynamic applications. With their versatility and reliability, flex circuit boards have become an essential component in various industries, including consumer electronics, automotive, medical devices, and aerospace.
FPC stands for Flexible Printed Circuit, which is a flexible circuit board made by using optical imaging, transfer, and etching processes on a flexible substrate. It consists of conductor circuit patterns created on the surface of a flexible material, with the outer and inner layers of double-sided and multilayer boards connected electrically through metalized holes. The circuit patterns are protected and insulated by PI and adhesive layers.
FPC boards can be classified into single-sided, windowed (also known as fingered), double-sided, multilayer, and rigid-flex boards.
PCB stands for Printed Circuit Board, which refers to rigid circuit boards.
Features of FPC:
1. Short assembly time: FPC boards have all the required circuitry, eliminating the need for additional wiring connections.
2. Small size: FPC boards have smaller dimensions compared to PCBs, allowing for reduced product size and increased portability.
3. Lightweight: FPC boards are lighter in weight than PCBs, contributing to the overall weight reduction of the final product.
4. Thinness: FPC boards are thinner than PCBs, enabling flexibility and three-dimensional assembly within limited space.
Advantages of FPC:
Flexible printed circuit boards offer several advantages that traditional rigid circuit boards lack:
1. Flexibility: FPC boards can be bent, rolled, and folded according to spatial requirements, allowing for integrated assembly of components and wire connections in three-dimensional space.
2. Size and weight reduction: FPC boards significantly reduce the size and weight of electronic products, catering to the increasing demand for high-density, miniaturized, and reliable electronic devices. They find wide applications in aerospace, military, mobile communication, laptops, computer peripherals, PDAs, digital cameras, and other fields.
3. Good heat dissipation and solderability: FPC boards exhibit good heat dissipation, solderability, and ease of assembly, along with lower overall costs. The combination of flexible and rigid materials compensates for the slight limitation of the flexible base material in component carrying capacity.
Disadvantages of FPC:
1. High initial cost: FPC boards designed and manufactured for specific applications involve higher initial costs for circuit design, routing, and photomask preparation. Unless there is a specific need for flexible PCBs, it is better to avoid their usage for small-scale applications.
2. Difficult to modify and repair: Once an FPC board is made, modifications require starting from the base design or the photomask program, making changes difficult. The protective film on the surface needs to be removed before repairs and then restored, adding to the complexity of the process.
3. Size limitations: FPC boards, especially those produced using intermittent processes, are limited by the size of production equipment, making it challenging to manufacture larger boards.
4. Susceptible to damage if mishandled: Improper handling during assembly can lead to damage to flexible circuits, making skilled personnel necessary for soldering and rework operations.
Main materials used in FPC:
The main materials used in FPC manufacturing include substrate, cover film, reinforcement materials, and other auxiliary materials.
Substrate:
1. Adhesive-based substrate: Adhesive-based substrates consist of three main components: copper foil, adhesive, and PI. They are classified into single-sided and double-sided substrates based on the presence of copper foil on one or both sides.
2. Non-adhesive-based substrate: Non-adhesive-based substrates do not have an intermediate adhesive layer. They only consist of copper foil and PI, offering advantages such as thinner, better dimensional stability, higher heat resistance, better flexibility, and better chemical resistance. They are widely used nowadays.
Copper foil: The commonly used copper foil thicknesses include 1oz, 1/2oz, and 1/3oz. Thinner copper foils with a thickness of 1/4oz have been introduced but are not widely used domestically, except for producing ultra-fine circuits with line widths and spacings of 0.05mm and below. As customer requirements increase, these specifications will likely be widely adopted in the future.
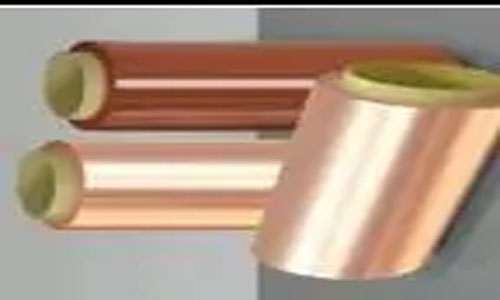
Cover film:
The cover film is composed of release paper, adhesive, and PI. Only the adhesive and PI layers remain on the product after the release paper is removed during the production process (the release paper's role is to protect against foreign objects on the adhesive).
Reinforcement materials:
Reinforcement materials are used in specific areas of an FPC to increase support strength and compensate for the flexible nature of the board. Commonly used reinforcement materials include:
1. FR4 reinforcement: It consists of glass fiber cloth and epoxy resin adhesive, similar to the FR4 material used in PCBs.
2. Steel plate reinforcement: It is composed of steel material and provides strong hardness and support strength.
3. PI reinforcement: It has the same composition as the cover film, including PI and adhesive release paper. The PI layer is thicker, ranging from 2MIL to 9MIL, depending on the specific production requirements.
Other auxiliary materials:
1. Pure adhesive: This adhesive film is a thermosetting acrylic adhesive film with a protective paper/release film and a layer of adhesive. It is used for laminated boards, rigid-flex boards, and FR-4/steel plate reinforcement boards for bonding purposes.
2. Electromagnetic shield film: This film is attached to the board surface for shielding purposes.
3. Pure copper foil: It consists of only copper foil and is mainly used in the production of windowed boards.
Types of FPC:
There are six types of FPC boards:
A. Single-sided: Circuitry present only on one side.
B. Double-sided: Circuitry present on both sides.
C. Windowed board: Also known as a fingered board due to opened windows on one side.
D. Multilayer: Circuitry present on separate layers.
E. Multilayer: Circuitry on two or more layers.
F. Rigid-flex board: A combination of flexible and rigid boards.
Contact: Pamela
Phone: +86 189 6365 3253
E-mail: info@industryprocess.com
Whatsapp:+86 189 6365 3253
Add: Yajing Industrial Park, No. 59 Shuangjing Street, Weiting Town, Suzhou Industrial Park
We chat