Optical film materials play a vital role in the photovoltaic industry, enabling efficient solar cell operation and light management. These innovative films, such as anti-reflective and transparent conductive polymer films, contribute to the overall performance, durability, and flexibility of solar cells. With the continuous development of thin-film and organic photovoltaic materials, the optoelectronic films used in the energy harvesting sector are constantly evolving. These advancements pave the way for sustainable and efficient energy solutions.
1. POL (Polaroid)
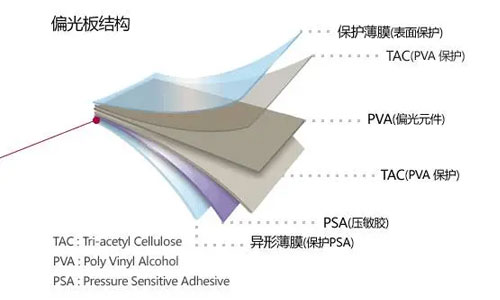
POL, or polarizing film, is a core material used in LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) technology. It is an optical film that allows light to pass through in a single direction while blocking light in the other direction.
2. FPR (Film-type Patterned Retarder)
FPR film transforms images into independent left-eye and right-eye circular polarizations, which can be viewed differently using polarized glasses. It is a key optical material used for 3D displays.

3. ITO (Indium Tin Oxide)
ITO film is a thin film deposited on a substrate material such as PET or COP using a sputtering process. It consists of a combination of indium and tin and is a crucial material used in touch panels.

4. CCL (Copper Clad Laminate)
CCL is a substrate material used for connecting circuitry in semiconductor chips and protecting them from external impacts.

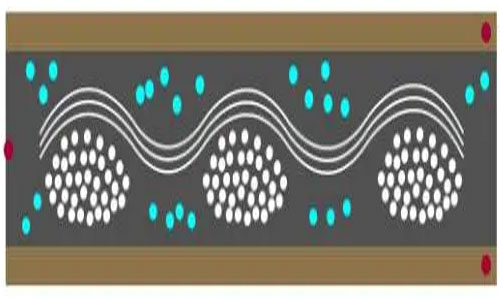
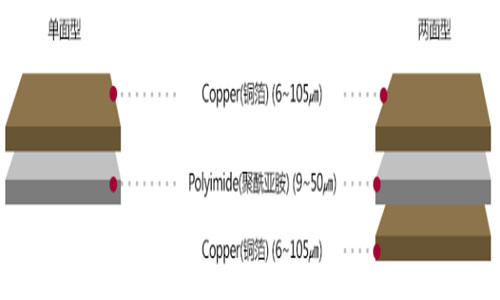
5. Layer FCCL (Adhesiveless Flexible Copper Clad Lamination)
Layer FCCL is a flexible circuit board material known for its excellent heat resistance, chemical stability, and bending flexibility. It is used to achieve miniaturization and high integration in mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets.

6. DAF (Die Attach Film)
DAF is a thin film used for bonding dies to substrates or dies to dies during semiconductor packaging.

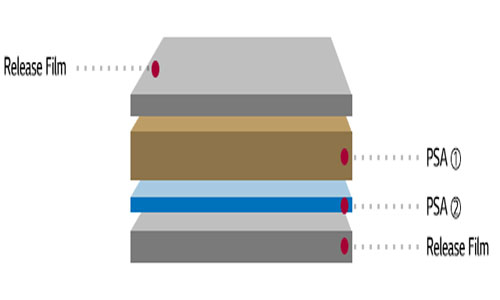
7. FSA (Face Sealing Adhesive)
FSA is a sealing material used in OLED packaging, greatly improving the lifespan of OLED displays.
In addition to the above, there are also optical film materials commonly used in backlight sources, including diffusion films, brightness enhancement films, reflector films, and quantum dot films.

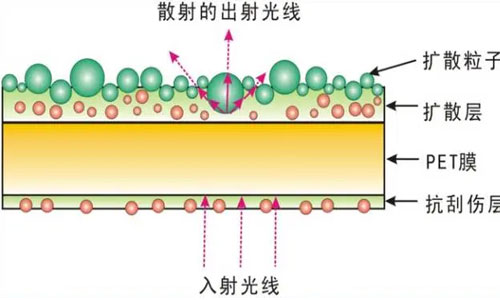
8. Diffusion Film
Diffusion films typically consist of three layers: a scratch-resistant layer at the bottom, a transparent PET substrate layer in the middle, and a diffusion layer on top. The diffusion film functions to scatter light and create a haze effect.
9. BEF (Brightness Enhancement Film)
Brightness enhancement films, also known as prism films, utilize micro-prism structures to redirect light and enhance brightness. They are transparent optical films consisting of three layers: a backlight incident surface with a certain level of haze provided by a back coating, a transparent PET substrate layer, and a top surface with micro-prism structures.
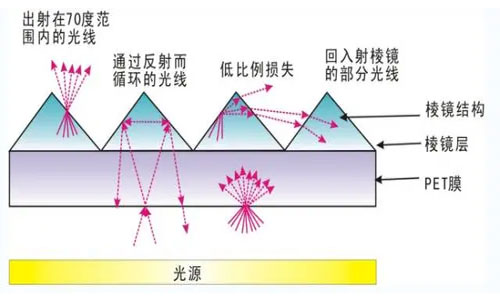
10. Reflector
Reflectors are usually placed at the bottom of backlight modules to redirect light that passes through the light guide plate back towards the panel, reducing light losses and increasing brightness.

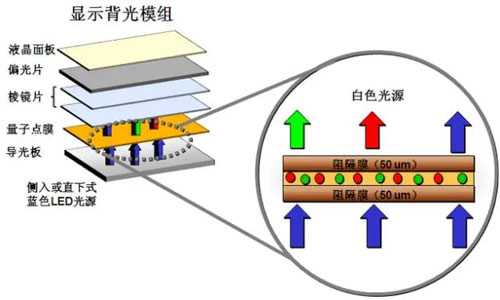
11. Q-DEF (Quantum Dot Enhancement Film)
Q-DEF is a film layer embedded with nano-sized spherical quantum dots made of indium phosphide and cadmium. It converts approximately two-thirds of the blue light emitted from the backlight source into pure red and green light.
Finally, protective films and release films are widely used in the production of optoelectronic displays. These films are made by coating a resin adhesive layer onto optically transparent PET films using ultra-precision coating technology. They include organic silicone adhesive series, polyurethane adhesive series, and acrylic adhesive series products.
Contact: Pamela
Phone: +86 189 6365 3253
E-mail: info@industryprocess.com
Whatsapp:+86 189 6365 3253
Add: Yajing Industrial Park, No. 59 Shuangjing Street, Weiting Town, Suzhou Industrial Park
We chat